Steam Login Overview
Log in is initiated by user action dependent on the client they are using. In the web-client this is a button press, while in the game client this happens automatically as part of the application start up. The user may be prompted to register a new Content Portal account during this process. The workflow ends by delivering the API authentication JWTs. Figure 1 illustrates this workflow.
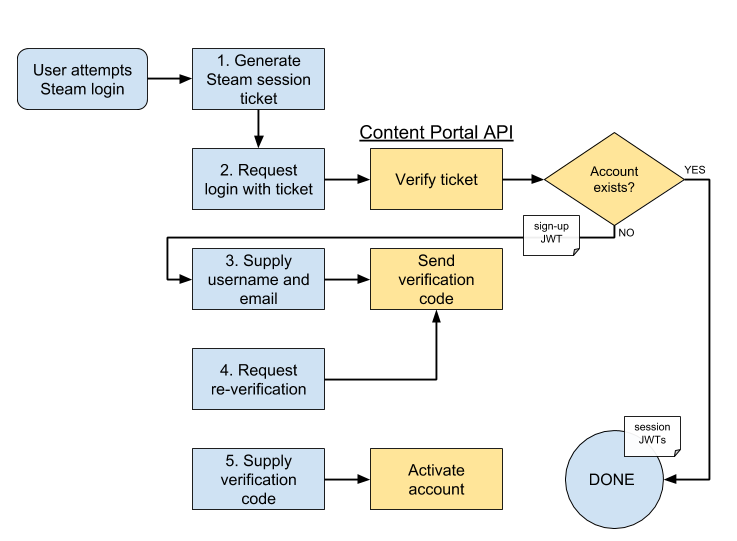
Steps
1. First, the user must acquire proof of their Steam account. In the game client, this takes the form of a session ticket. On the web client, the user completes Steam's OpenID workflow (linking to Steam's log in form, logging in, and being redirected back to the source), yielding an OpenID 2.0 "assertion". (API method GET /auth/steam/authenticate is used to craft an appropriate initial link for the OpenID workflow.)
2. The proof is sent to the appropriate Steam API as a login request:
- POST /auth/steam/ticket-login for the game client
- POST /auth/steam/login for the web client
The Content Portal verifies the provided identity proof, then checks to see if that Steam user corresponds to a known Endless account.
If so, the login process is completed: a session record is created and stored, and the set of JWTs for that session are sent back to the user.
If such an account does not exist, the user must continue with the account creation workflow. A special sign-up JWT is created and returned to the user. This token is short-lived and limited to the bare minimum API methods needed to complete account creation.
3. The user is prompted to provide a user name for their Endless account, as well as their email address. This is sent to POST /auth/steam/create along with the sign-up JWT. The API stores this information and then sends a verification code to the user via email.
4. The user may at any point request a new verification code: POST /auth/email/reverify NOTE: not yet implemented.
5. If the user supplies the correct verification code before its expiration (POST /auth/email/verify), the user account is fully activated. The user must then re-attempt the login process to access their account.
Of course, this only diagrams the successful outcomes of all requests. Normal error responses may be issued for situations like invalid or expired proof of identity, user name is taken, sign-up token invalid or expired, verification code incorrect or expired, etc.